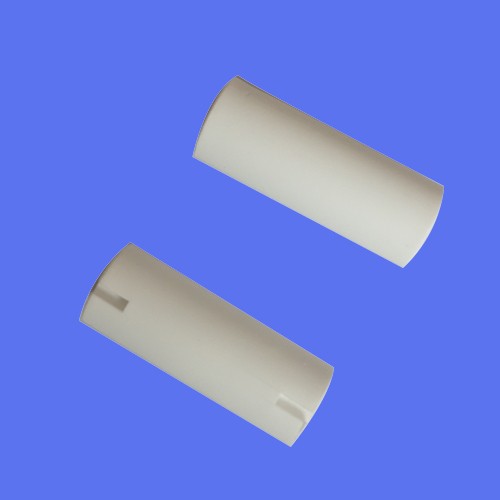
Injection molding of alumina ceramic tube
Alumina ceramic tubes have excellent properties such as high mechanical strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, high thermal conductivity and resistivity. They are widely used in high technology and industry, such as microelectronics, nuclear reactor, magnetohydrodynamic power generation, aerospace, artificial bone and bone joint.
For alumina ceramic products with high dimensional accuracy and complex shape, injection molding has a special technical advantage compared with the traditional molding process with high machining cost. As a kind of near net forming technology, ceramic injection molding has the advantages of accurate and controllable product size, high mechanical degree, easy to achieve mass production, no or only a small amount of machining, which greatly reduces the production cost of ceramics.
Compared with traditional molding methods, ceramic injection molding technology has the following advantages:
(1) High degree of mechanization and automation of forming process.
(2) The ceramic parts with various complex shapes can be shaped near net, so that the sintered ceramic products do not need machining or less machining, so as to reduce the expensive ceramic processing cost;
(3) The shaped ceramic products have high dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Injection process of alumina ceramics
Ceramic injection molding process mainly includes four processes: feeding, injection molding, degreasing and sintering.
(1) Powder selection and optimization
It was found that different Al2O3 powder mixing ratio resulted in different binder ratio, feed fluidity, product shrinkage and grain boundary diffusion. The composite materials prepared by doping other ceramic or metal materials with alumina as the base and Cr3C2, SiC, Ti, WC, ZrO2, Al and MgO in alumina can enhance dislocation and control grain growth, facilitate grain refinement and improve mechanical properties of products.
Another research area of powder preparation is the influence of powder average particle size, bulk density, powder shape, specific surface area, particle gap on feed flow performance and product quality. Powder as the main material of injection molding, the important requirement is small particle size and regular shape. The powder with small particle size has good fluidity, large filling amount and low sintering shrinkage during injection molding.
(2) Binder
Selection of binder
The selection of binder system is the key link in the injection molding of alumina ceramics. It not only directly affects the injection performance of the feedstock, but also determines the degreasing method and product performance. The binder system has two basic functions in the process of injection molding: first, to ensure that the feed has good fluidity; second, to ensure the strength of the body.
At present, the commonly used binder in the injection molding of alumina ceramics is composed of paraffin (PW), polypropylene (PP) and hard acid (SA).
Influence of surfactants
According to the theory of rheology, surfactants control the properties of ceramic feed to a great extent, and the stability of feed will increase with the thickness of absorption layer on the surface of ceramic particles. In the injection molding process of alumina ceramics, the amount of surfactant will change with the other components of the binder, and its content is mostly between 1% and 5%.
(3) Degreasing
Degreasing process is not only a time-consuming process in injection molding process, but also a key process in quality control. Improper degreasing will cause many product defects. A lot of research work shows that the degreasing process is closely related to the addition of binder, and the degreasing methods adopted are different with different binders.
(4) Sintering
After degreasing, the ceramic blank is porous and low density. It needs to be densified and sintered at high temperature to obtain the required dimensional accuracy and fiber structure of the compact ceramic parts.
previous page:Toughening technology of alumina ceramic ring
next page:What can alumina ceramics be used for?

What are the sintering and functions of alumina ceramics?
The strength of alumina ceramics is only a millionth different from that of diamond. However, if alumina ceramics and wear-resistant steel, or stainless steel plates are used to develop wear resistanc...
Time of publication:2019-12-19
Changes of alumina ceramic structure at high temperature
Alumina ceramics is a kind of ceramics with alumina as the core, which is characterized by super high hardness, light weight, high heat conduction, high brittleness and wear resistance. Because cerami...
Time of publication:2019-12-18
Toughening technology of alumina ceramic ring
Toughening technology of alumina ceramic ringMetal materials are easy to produce plastic deformation, because the metal bond is not directional. In ceramic materials, the bond between atoms is covalen...
Time of publication:2019-12-14
Injection molding of alumina ceramic tube
Alumina ceramic tubes have excellent properties such as high mechanical strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, high thermal conductivity and resistivity. They ar...
Time of publication:2019-12-10
What is the difference between alumina ceramics and ordinary ceramics?
Alumina ceramic is a kind of ceramic material with alumina (Al2O3) as the main body, which is used in thick film integrated circuit. Alumina ceramics have good conductivity, mechanical strength and hi...
Time of publication:2019-12-10
What can alumina ceramics be used for?
Application of alumina ceramics 1. Mechanical The bending strength of Al2O3 sintered products can reach 250Mpa, and that of hot pressed products can reach 500MPa...
Time of publication:2019-12-09
What are the preparation methods of alumina ceramics?
Preparation of alumina ceramics 1. Preparation of powderAluminum oxide powder is prepared into powder materials according to different product requirements and different molding pr...
Time of publication:2019-12-09
Introduction of sintering process of alumina ceramics
Introduction of sintering process of alumina ceramics 1. Atmospheric sinteringSintering at atmospheric pressure means that materials are sintered under atmospheric pres...
Time of publication:2019-12-09
Column navigation/Column menu
1What are the sintering and functions of alumina ceramics?
2019-12-19

2Changes of alumina ceramic structure at high temperature
2019-12-18

3Toughening technology of alumina ceramic ring
2019-12-14

4Injection molding of alumina ceramic tube
2019-12-10

5What is the difference between alumina ceramics and ordinary ceramics?
2019-12-10

6What can alumina ceramics be used for?
2019-12-09